What is an Electrical Vehicle Charging point?
Electric vehicle supply equipment is a key component in the roll-out of charging infrastructure for EV’s using a conductive or wireless charging solution.
How does EV charging work at home?
Most EVs can charge from a three pin socket using the mode 2 charging equipment supplied with the vehicle. But more sophisticated EVSE is being installed in residential, business and public infrastructure, providing charging management capabilities as access control, configurable charging power and accountability for charging events.
There are different modes of charging:
Mode 1: Connection of the EV to the AC supply network utilizes socket outlets not exceeding 16 A and not exceeding 250 V AC single phase or 480 V AC for three phase supply utilizing power and protective earth conductors.

Mode 1 Vehicle Charging
The 4th Edition of The IET Code of Practice for Electric Vehicle Charging 2020. ISBN 978-1-85953-180-4 (paperback).
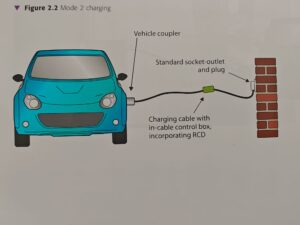
Mode 2: Is similar to mode 1 just that it provide charging currents of 10 A or less. Being feed from a socket outlet with max 32 A and not exceeding 250VAC or three phase 480 V AC. Utilizes the power and protective earth conductors together with a control pilot and system of personnel protection against electric shock between ev charger and in cable control box.
One of the most important things when you want to have an Electrical Vehicle charger Installed is to Contact an Electrician to carry a Survey at your property in order, to see the setup of the Fuse Supplying your house.
Electrical Vehicle Chargers require that your house have a 100 AMPS Cut out Fuse. Should it not be the case then an upgrade from DNO is required (your electrician can request the upgrade for you).
How Does EV Charging work at home?
Very simple once the ev Charger is installed at your house, simply plug your car in and charge it.
What is kW, kWh, and charging speed explained simply?
kW (kilowatt) = Power (Speed)
Think of kW like the speed of water coming out of a tap.
-
It tells you how fast energy is being delivered
-
In EV charging, it means how fast the car is charging
Example:
-
7kW charger = slower
-
22kW charger = faster
-
50kW / 150kW charger = very fast
kW = rate of charging
kWh (kilowatt-hour) = Energy (Size of the battery)
Think of kWh like the size of a water tank.
-
It tells you how much energy is stored
-
In EVs, it’s the battery capacity
Example:
-
40kWh battery = smaller range
-
75kWh battery = bigger range
-
100kWh battery = long range
kWh = how much energy you have
Bibliography:
The 4th Edition of The IET Code of Practice for Electric Vehicle Charging 2020. ISBN 978-1-85953-180-4 (paperback).








